CONSULTANCY
Pure Visions see two fundamental areas where our consultancy services can be effective for your business.
The first is to provide expert advice in the areas in which we specialise. The experience of our professional consultants means that we are ideally placed to provide our clients with the knowledge, information, and advice they require.
The second is to offer clients the benefit of our considerable professional experience in refocusing their business or a specific aspect of their business.
Through our Consultancy Service, we help set your business on the right track. Where there is a skills/knowledge gap we fill it.
The world never stands still. There are always new ideas, new technologies and new opportunities. Organizations need to continuously adapt to remain competitive. To do this, they must learn. And organizations, like individuals, learn from experience - both their own and of others. At EFQM, we believe in a world where organizations share their ideas, experience and learning to help achieve sustainable economic development. After all, a strong, stable global economy benefits us all.

ADEP works on sustain improvement in government entities through the development and implementation of innovative programs and initiatives. Developing the principles and standards for the Abu Dhabi Excellence Award in Government Performance in identifying areas for improvement. And to ensure a culture of excellence by adhering to its principles and requirements in improvement. Additional to that ADEP also Monitor the customer satisfaction index and provide research, studies and best practices related to the provision and excellence of services.

Sheikh Khalifa Excellence Award (SKEA); 14 years of sustainable Excellence
The Sheikh Khalifa Excellence Award (SKEA) was launched by the Abu Dhabi Chamber of Commerce & Industry (ADCCI) back in 1999 as a blue print, a roadmap and a methodology for continuous improvement aimed at enhancing the competitiveness of the Business Sector in Abu Dhabi and the UAE.
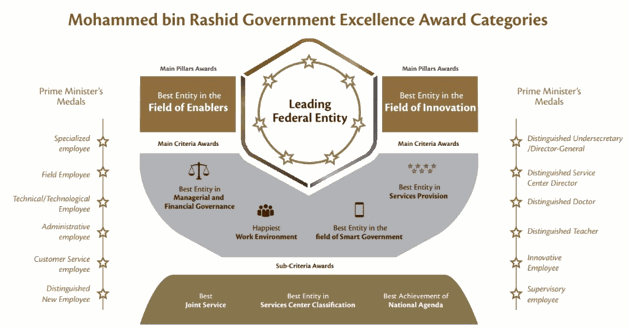
 The Mohammed bin Rashid Government Excellence Award is divided into five different categories and 22 awards that take into account the diversity in the work nature of federal entities and achievements of the Sheikh Khalifa Government Excellence Program’s objectives and leadership in all fields. The Mohammed bin Rashid Government Excellence Award categories also differs with respect to the application method used. Below is a list of the different award categories:
The Mohammed bin Rashid Government Excellence Award is divided into five different categories and 22 awards that take into account the diversity in the work nature of federal entities and achievements of the Sheikh Khalifa Government Excellence Program’s objectives and leadership in all fields. The Mohammed bin Rashid Government Excellence Award categories also differs with respect to the application method used. Below is a list of the different award categories:
Our Services
-
Organizational Development and Excellence
-
Development Planning
-
Quality Management and International Standards
-
Development of Human Resources
-
Process Engineering
-
Studies, Surveys and Projects
-
Environmental Management and Sustainable Energy
-
Management of Information Technology
Inspection, Testing & Examination
-
Lifting Equipment Inspection
-
Lifting Gears Inspection
-
Industrial Trucks Inspection
-
Earth Moving Machineries Inspection
-
Non-Destructive Test
The ISO 9000 family addresses various aspects of quality management and contains some of ISO’s best known standards. The standards provide guidance and tools for companies and organizations who want to ensure that their products and services consistently meet customer’s requirements, and that quality is consistently improved.
Standards in the ISO 9000 family include:
-
ISO 9001:2015 - sets out the requirements of a quality management system
-
ISO 9000:2015 - covers the basic concepts and language
-
ISO 9004:2009 - focuses on how to make a quality management system more efficient and effective
-
ISO 19011:2011 - sets out guidance on internal and external audits of quality management systems.
ISO 9001:2015
ISO 9001:2015 sets out the criteria for a quality management system and is the only standard in the family that can be certified to (although this is not a requirement). It can be used by any organization, large or small, regardless of its field of activity. In fact, there are over one million companies and organizations in over 170 countries certified to ISO 9001.
This standard is based on a number of quality management principles including a strong customer focus, the motivation and implication of top management, the process approach and continual improvement.
Certification to ISO 9001:2015
Checking that the system works is a vital part of ISO 9001:2015. It is recommended that an organization performs internal audits to check how its quality management system is working.
Sector-specific applications of ISO 9001
ISO has a range of standards for quality management systems that are based on ISO 9001 and adapted to specific sectors and industries. These include:
- ISO/TS 29001 – Petroleum, petrochemical and natural gas industries
- ISO 13485 – Medical devices
- ISO/IEC 90003 – Software engineering
- ISO 17582 – Electoral organizations at all levels of government
- ISO 18091 - Local government
The ISO 14000 family of standards provides practical tools for companies and organizations of all kinds looking to manage their environmental responsibilities.
ISO 14001:2015 and its supporting standards such as ISO 14006:2011 focus on environmental systems to achieve this. The other standards in the family focus on specific approaches such as audits, communications, labelling and life cycle analysis, as well as environmental challenges such as climate change.
The ISO 14000 family of standards are developed by ISO Technical Committee ISO/TC 207 and its various subcommittees.
ISO 14001:2015
ISO 14001:2015 sets out the criteria for an environmental management system and can be certified to. It maps out a framework that a company or organization can follow to set up an effective environmental management system. It can be used by any organization regardless of its activity or sector.
Using ISO 14001:2015 can provide assurance to company management and employees as well as external stakeholders that environmental impact is being measured and improved.
Over 6300 people die each day from work-related accidents or diseases - that’s nearly 2.3million every year.
The burden of occupational injuries and diseases is significant, both for employers and the wider economy, resulting in losses from early retirements, staff absence and rising insurance premiums.
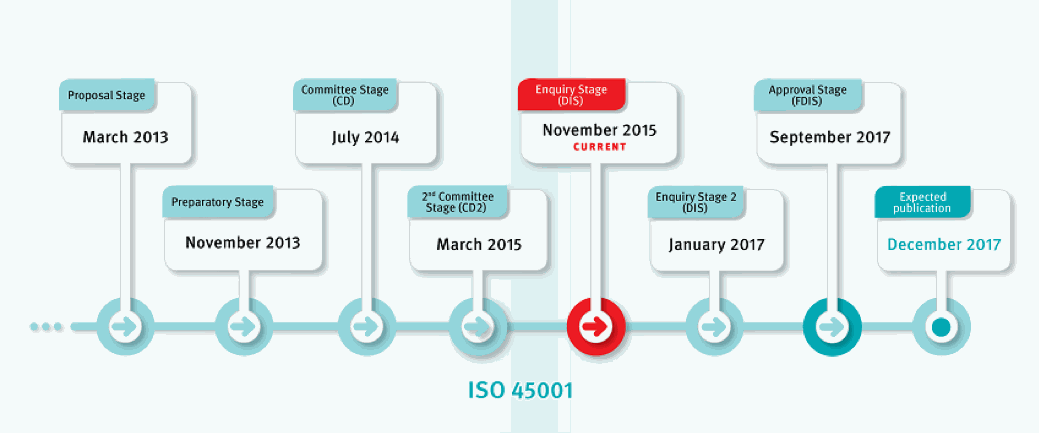
To combat the problem, ISO is developing a new standard, ISO 45001 Occupational health and safety management systems - Requirements, that will help organizations reduce this burden by providing a framework to improve employee safety, reduce workplace risks and create better, safer working conditions, all over the world.
The standard is currently being developed by a committee of occupational health and safety experts, and will follow other generic management system approaches such as ISO 14001 and ISO 9001. It will take into account other International Standards in this area such as OHSAS 18001, the International Labour Organization's ILO-OSH Guidelines, various national standards and the ILO's international labour standards and conventions.
Business and organizations do not operate in a vacuum. Their relationship to the society and environment in which they operate is a critical factor in their ability to continue to operate effectively. It is also increasingly being used as a measure of their overall performance.
ISO 26000 provides guidance on how businesses and organizations can operate in a socially responsible way. This means acting in an ethical and transparent way that contributes to the health and welfare of society.
ISO 26000:2010
ISO 26000:2010 provides guidance rather than requirements, so it cannot be certified to unlike some other well-known ISO standards. Instead, it helps clarify what social responsibility is, helps businesses and organizations translate principles into effective actions and shares best practices relating to social responsibility, globally. It is aimed at all types of organizations regardless of their activity, size or location.
The standard was launched in 2010 following five years of negotiations between many different stakeholders across the world. Representatives from government, NGOs, industry, consumer groups and labour organizations around the world were involved in its development, which means it represents an international consensus.
Using energy efficiently helps organizations save money as well as helping to conserve resources and tackle climate change. ISO 50001 supports organizations in all sectors to use energy more efficiently, through the development of an energy management system (EnMS).
ISO 50001:2011 – Energy Management System
ISO 50001 is based on the management system model of continual improvement also used for other well-known standards such as ISO 9001 or ISO 14001. This makes it easier for organizations to integrate energy management into their overall efforts to improve quality and environmental management.
ISO 50001:2011 provides a framework of requirements for organizations to:
-
Develop a policy for more efficient use of energy
-
Fix targets and objectives to meet the policy
-
Use data to better understand and make decisions about energy use
-
Measure the results
-
Review how well the policy works, and
-
Continually improve energy management.
Risks affecting organizations can have consequences in terms of economic performance and professional reputation, as well as environmental, safety and societal outcomes. Therefore, managing risk effectively helps organizations to perform well in an environment full of uncertainty.
ISO 31000:2009
ISO 31000:2009, Risk management – Principles and guidelines, provides principles, framework and a process for managing risk. It can be used by any organization regardless of its size, activity or sector. Using ISO 31000 can help organizations increase the likelihood of achieving objectives, improve the identification of opportunities and threats and effectively allocate and use resources for risk treatment.
However, ISO 31000 cannot be used for certification purposes, but does provide guidance for internal or external audit programmes. Organizations using it can compare their risk management practices with an internationally recognised benchmark, providing sound principles for effective management and corporate governance.
Related Standards
A number of other standards also relate to risk management:
-
ISO Guide 73:2009, Risk management - Vocabulary complements ISO 31000 by providing a collection of terms and definitions relating to the management of risk.
-
ISO/IEC 31010:2009, Risk management – Risk assessment techniques focuses on risk assessment. Risk assessment helps decision makers understand the risks that could affect the achievement of objectives as well as the adequacy of the controls already in place. ISO/IEC 31010:2009 focuses on risk assessment concepts, processes and the selection of risk assessment techniques.
The ISO 22000 family of International Standards addresses food safety management. The consequences of unsafe food can be serious and ISO’s food safety management standards help organizations identify and control food safety hazards. As many of today's food products repeatedly cross national boundaries, International Standards are needed to ensure the safety of the global food supply chain.
The ISO 22000 family contains a number of standards each focusing on different aspects of food safety management.
-
ISO 22000:2005 contains the overall guidelines for food safety management.
-
ISO 22004:2014 provides generic advice on the application of ISO 22000
-
ISO 22005:2007 focuses on traceability in the feed and food chain
-
ISO/TS 22002-1:2009 contains specific prerequisites for food manufacturing
-
ISO/TS 22002-2:2013 contains specific prerequisites for catering
-
ISO/TS 22002-3:2011 contains specific prerequisites for farming
-
ISO/TS 22002-4:2013 contains specific prerequisites for food packaging manufacturing
-
ISO/TS 22003:2013 provides guidelines for audit and certification bodies
ISO 22000 is under revision
ISO 22000, Food safety management systems -- Requirements for any organization in the food chain is under revision, with the draft version available for purchase from early 2017.
The final updated version is expected late 2018.
ISO 22000:2005
ISO 22000:2005 sets out the requirements for a food safety management system and can be certified to. It maps out what an organization needs to do to demonstrate its ability to control food safety hazards in order to ensure that food is safe. It can be used by any organization regardless of its size or position in the food chain.
The ISO/IEC 27000 family of standards helps organizations keep information assets secure.
Using this family of standards will help your organization manage the security of assets such as financial information, intellectual property, employee details or information entrusted to you by third parties.
ISO/IEC 27001 is the best-known standard in the family providing requirements for an information security management system (ISMS).
What is an ISMS?
An ISMS is a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information so that it remains secure. It includes people, processes and IT systems by applying a risk management process.
It can help small, medium and large businesses in any sector keep information assets secure.
Certification to ISO/IEC 27001
Like other ISO management system standards, certification to ISO/IEC 27001 is possible but not obligatory. Some organizations choose to implement the standard in order to benefit from the best practice it contains while others decide they also want to get certified to reassure customers and clients that its recommendations have been followed. ISO does not perform certification.
Bribery is one of the world’s most destructive and challenging issues. With over US$ 1 trillion paid in bribes each year*, the consequences are catastrophic, reducing quality of life, increasing poverty and eroding public trust.
Yet despite efforts on national and international levels to tackle bribery, it remains a significant issue. Recognizing this, ISO has developed a new standard to help organizations fight bribery and promote an ethical business culture.
ISO 37001, Anti-bribery management systems, specifies a series of measures to help organizations prevent, detect and address bribery. These include adopting an anti-bribery policy, appointing a person to oversee anti-bribery compliance, training, risk assessments and due diligence on projects and business associates, implementing financial and commercial controls, and instituting reporting and investigation procedures.
It is designed to help your organization implement an anti-bribery management system, or enhance the controls you currently have. It helps to reduce the risk of bribery occurring and can demonstrate to your stakeholders that you have put in place internationally recognized good-practice anti-bribery controls.
Who is it for?
ISO 37001 can be used by any organization, large or small, whether it be in the public, private or voluntary sector, and in any country. It is a flexible tool, which can be adapted according to the size and nature of the organization and the bribery risk it faces.
Safety and quality are non-negotiables in the medical devices industry. Regulatory requirements are increasingly stringent throughout every step of a product’s life cycle, including service and delivery. More and more, organizations in the industry are expected to demonstrate their quality management processes and ensure best practice in everything they do.
ISO 13485, Medical devices – Quality management systems – Requirements for regulatory purposes, is an internationally agreed standard that sets out the requirements for a quality management system specific to the medical devices industry. It has recently been revised, with the new version published in March 2016.
What is a medical device?
A medical device is a product, such as an instrument, machine, implant or in vitro reagent, that is intended for use in the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of diseases or other medical conditions.
Who is ISO 13485 for?
ISO 13485 is designed to be used by organizations involved in the design, production, installation and servicing of medical devices and related services. It can also be used by internal and external parties, such as certification bodies, to help them with their auditing processes.
Certification to ISO 13485
Like other ISO management system standards, certification to ISO 13485 is not a requirement of the standard, and organizations can reap many benefits from implementing the standard without undergoing the certification process. However, third-party certification can demonstrate to regulators that you have met the requirements of the standard. ISO does not perform certification.
What are the key improvements?
The new version has a greater emphasis on risk management and risk-based decision making, as well as changes related to the increased regulatory requirements for organizations in the supply chain.
Personnel certification has become an important element of verifying the competence of an increasingly mobile and global workforce, underscoring the value of industry-recognized credentials that can be carried across national borders. In response to this growing need, a new and improved ISO/IEC International Standard aims to harmonize the various procedures used around the world for certifying the competence of personnel in different occupations or professions.
ISO/IEC 17024:2012, Conformity assessment – General requirements for bodies operating certification of persons, provides a global benchmark for personnel certification programmes to ensure that they operate in a consistent, comparable and reliable manner worldwide, thereby allowing individuals to have skills that translate across national lines.
The breadth and scope of certification programmes in existence today is tremendous: programs exist for financial planners, public accountants, safety professionals, non-destructive testing experts, supply and purchasing management professionals, the construction industry, health care professionals and hundreds more.
The updated ISO/IEC 17024:2012 standard will help organizations that certify individuals in a variety of occupations and professions protect the integrity and ensure the validity of individual certification programmes. It will also promote consumer and public confidence in the capabilities and competence of the people who provide specialized services or who create the products that support our daily lives and livelihoods.
“Most professionals now pursue certification as a means of demonstrating that they have the necessary knowledge, skills and abilities to perform their work,” explains Dr. Cynthia Woodley, Chair of the team that developed the new standard. “Programmes accredited under ISO/IEC 17024 will increase the potential for national and international reciprocity of certified individuals and personnel certification bodies.”
In this second edition, the framework outlined in ISO/IEC 17024 has been reviewed and updated to take account of new requirements for personal certification programmes and security-related issues. New criteria for examinations were also added.
The new ISO/IEC 17024 standard addresses the structure and governance of the certifying body, the characteristics of the certification programme, the information required to be available to applicants, and the recertification initiatives of the certifying body. It is designed to help organizations conduct well-planned and structured evaluations in order to ensure impartiality of operations and reduce any conflict of interest.
Conformity assessment -- Requirements for the operation of various types of bodies performing inspection
ISO/IEC 17020:2012 specifies requirements for the competence of bodies performing inspection and for the impartiality and consistency of their inspection activities.
It applies to inspection bodies of type A, B or C, as defined in ISO/IEC 17020:2012, and it applies to any stage of inspection.
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) and IEC (the International Electrotechnical Commission) form the specialized system for worldwide standardization. National bodies that are members of ISO or IEC participate in the development of International Standards through technical committees established by the respective organization to deal with particular fields of technical activity. ISO and IEC technical committees collaborate in fields of mutual interest. Other international organizations, governmental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO and IEC, also take part in the work. In the field of conformity assessment, the ISO Committee on conformity assessment (CASCO) is responsible for the development of International Standards and Guides.
International Standards are drafted in accordance with the rules given in the ISO/IEC Directives, Part 2.
Draft International Standards are circulated to the national bodies for voting. Publication as an International Standard requires approval by at least 75 % of the national bodies casting a vote.
Attention is drawn to the possibility that some of the elements of this document may be the subject of patent rights. ISO shall not be held responsible for identifying any or all such patent rights.
ISO/IEC 17020 was prepared by the ISO Committee on conformity assessment (CASCO).
It was circulated for voting to the national bodies of both ISO and IEC, and was approved by both organizations.
This second edition cancels and replaces the first edition (ISO/IEC 17020:1998), which has been technically revised.
Conformity assessment -- Requirements for the operation of various types of bodies performing inspection
ISO/IEC 17020:2012 specifies requirements for the competence of bodies performing inspection and for the impartiality and consistency of their inspection activities.
It applies to inspection bodies of type A, B or C, as defined in ISO/IEC 17020:2012, and it applies to any stage of inspection.
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) and IEC (the International Electrotechnical Commission) form the specialized system for worldwide standardization. National bodies that are members of ISO or IEC participate in the development of International Standards through technical committees established by the respective organization to deal with particular fields of technical activity. ISO and IEC technical committees collaborate in fields of mutual interest. Other international organizations, governmental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO and IEC, also take part in the work. In the field of conformity assessment, the ISO Committee on conformity assessment (CASCO) is responsible for the development of International Standards and Guides.
International Standards are drafted in accordance with the rules given in the ISO/IEC Directives, Part 2.
Draft International Standards are circulated to the national bodies for voting. Publication as an International Standard requires approval by at least 75 % of the national bodies casting a vote.
Attention is drawn to the possibility that some of the elements of this document may be the subject of patent rights. ISO shall not be held responsible for identifying any or all such patent rights.
ISO/IEC 17020 was prepared by the ISO Committee on conformity assessment (CASCO).
It was circulated for voting to the national bodies of both ISO and IEC, and was approved by both organizations.
This second edition cancels and replaces the first edition (ISO/IEC 17020:1998), which has been technically revised.
RE-Support is a technical team who can provide on-line support to solve specific RE technical issues. This service is presented for clients within the Middle East region as it does not require traveling. The team will provide the technical advice either by e-mail or via phone call. For further clarification about providing this service you can contact Info@genceco.com The following are examples for these technical issues: QA/QC needed from each discipline to continue the modelling loop Type of integration needed between different disciplines Issues related to well performance and design
POS is the process of looking to well and reservoir data and analyzes them in an integrated approach with multiple surface and subsurface disciplines. The objectives of the team who will perform such studies are to increase production, enhance recovery, while lowering costs.
IRS is a combination and co-ordination of separate and diverse elements or units into a more complete or harmonious method of working. Therefore it is considered as a process whereby extra value is produced. In the petroleum industry, integration primarily concerned with the manner in which different disciplines efforts are combined to improve an established analytical process.
Matured oil fields are basically suffering from high water production rates. Part of this water is good water and part is bad water. WRS is a process that we can apply to diagnose where we can decrease the amount of the bad water, hence reducing the cost per barrel of oil produced.
EPQS is a process defined by a group of highly experienced people. The process consists of proprietary analysis techniques aimed to analyzing the reservoir data on a large scale and in a short time frame. This analysis will help the operators to select the best candidates for work-over and the best location to drill infill wells
RSS is an area of reservoir engineering in which computer models are developed to model physical phenomena involved during flow in porous media. These models are essential for the understanding of reservoir processes (oil, gas and water flow). Number of methods and tools are used for this purpose, varying from commercial reservoir simulators to specially developed and dedicated models. For further clarification about providing these services
you can contact info@pure-visions.com
makes the history matching (HM) of reservoir simulation models faster, more reliable, easier, and more accurate while assuring consistency between the interpreted and refined source data and the simulation model.
LYNX provides the asset team with powerful analysis aids to facilitate the interactive HM process. Engineers have carried out history matching through simulation for over 40 years.
LYNX now provides the engineer with a tool that significantly streamlines and accelerates the history matching process. Developing and history matching reservoir models is data intensive requiring petrophysics, geology, production, fluid, and rock information to be processed and interpreted into a coherent geologic and simulation model of the reservoir. A reservoir simulator is then used to test this model against actual performance data (fluid rates, pressures, and concentrations). Inconsistencies in the simulation model versus actual performance must be reconciled and adjustments made to the reservoir model.
LYNX provides the practical tools and workflow to review and resolve these inconsistencies quickly and to make the necessary adjustments in a manner that is consistent with all other relevant data. This is achieved by the property modification facilities that substantially eliminate the manual editing of the simulation data set.
LYNX is designed with a complementary set of tools for interacting with commercial
MatchingPro® is the latest innovative history matching (HM) technology from NITEC that is very easy to use, fully utilizes available computing resources, and provides fast, reliable HM solutions. MatchingPro only requires a reservoir simulation modelcombined with historical production, injection, and pressure data to accurately and efficiently determine the best HM solution based on the selected HM parameters.
MatchingPro® can function in auto or manual modes to achieve a high quality HM solution. In the MatchingPro auto mode, simulation cases are designed, run, and evaluated without user intervention. The number of simulation cases required is typically six to eight times the number of HM parameters. HM quality measurements are updated and displayed with each new simulation case that is run. The process is expedited by utilizing multiple computer CPUs, when available.
MatchingPro®’s cutting edge technology makes use of Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), Genetic Algorithms (GA), and statistical methods. These algorithms quickly reveal the complex relationships among the HM parameters and the simulation results (the mismatch in simulated versus historical volumes and pressures).
MatchingPro® quantifies the quality of each HM case and recommends the best combination of HM parameters to achieve the best HM solution.
MatchingPro® can also determine multiple HM solutions (model characterizations) and provide a quantification of their probabilities of occurrence. Reservoir simulation is a key tool in the asset manager’s quest to maximiz recoveries and enhance reserves. History matching of reservoir simulation models is a critical step in the reservoir evaluation and field development process.
- Reservoir Management Study
- Integrated Field Management
- Integrated Reservoir Studies
- Reserves Evaluation Study
- Field Development Plan
- Reservoir simulation
PURPOSE OF THE STUDY:
Optimize oil, water and gas production to maintain the reservoir pressure and improve oil production.
SUMMARY
The principles of sound reservoir management are implemented with emphasis on practical applications.An interdisciplinary synergistic approach to efficiently manage the reservoir is detailed with the goal of optimum profitability.The significance of each component of the study and importance of timing and cost/benefit analysis are executed and checked between different subsurface disciplines.Reservoir management models for optimum field development plans and field operating plans are analyzed. The interdisciplinary reservoir management approach shows how each technology contributes to the plan and how QAQC and balances are developed.
PURPOSE OF THE STUDY:
Increased oil production and lowered lifting cost in mature fields
SUMMARY
GENCE & EPTS have a good experience in implementing such study. The study will include four main steps:
-
Reservoir performance analysis:
This study will be performed to understand the driving mechanism of the reservoir and the potential areas/zones that might respond to work-over positively. This will be achieved either by applying simple material balance using material balance software for the reservoir or by applying EPQS process to the full field “add link. The main objective of this study is to check the deliverability and reserves of the reservoir.
-
Artificial lift analysis:
This will be done by constructing A/L models using the client preferred software for producing wells to understand the performance efficiency of these wells. This will be achieved by modelling the lift performance for the current oil producers. The main objective of this study is to diagnose the well performance problems and propose solutions. The deliverables for this study will be clear recommendations to the operations department to perform successful work-over to the wells and produce with better and economic oil rates.
-
Surface facility analysis:
This will be done by constructing surface network model for the surface facilities in the field. The model will propose if there are any bottle necks in the surface system.
-
Apply Integrated Production Modeling Approach:
The previous models will be integrated together to better understand the full system. The integrated system will be optimized to get the maximum oil production from the system, in addition clear recommendations will be advised to which part of the system is better to be intervened.
PURPOSE OF THE STUDY:
Locate Bypassed and Untapped Oil Describe Current Reservoir Conditions Predict Reservoir Performance Under Different Development Scenarios
SUMMARY
Phase-I Static Models Construction
-
SEISMIC INTERPRETATION/REVIEW:
EPTS team will either interpret or review the available interpretation according to highest standard, then decision will be taken to come up with the most realistic interpretation cases to represent the different reservoirs in the field. The team will also determine the uncertainties associated to these interpretations. If multiple scenarios need to be considered, then the team will construct them if needed.
-
PETROPHYSICAL INTERPRETATION/REVIEW:
EPTS team will start applying it’s QC process for the open/cased-hole log data available and will come up with decision for the best method for interpreting such data. The most realistic results will be integrated with EPTS team and if necessary different set of reservoir properties will be considered for the full field static model. The team will also determine the amount of uncertainties associated to these interpretations.
-
GEOLOGICAL INTERPRETATION/REVIEW:
EPTS team will start applying it’s QC process for the available geological data. Well correlation panels will be constructed then integrated with the team. The most realistic correlation will be considered to build the structural model. This model will be validated by the engineering team in the following phases of the study.
-
SEDIMENTLOGICAL INTERPRETATION/REVIEW:
EPTS team will check the general geological setting and review main depositional setting for the studied reservoir to come up with the best models to represent the distribution of different facies in the model. This distribution will be validated against the available core, logs, pressure, and production data.
-
STATIC MODEL CONSTRUCTION:
EPTS team will construct the static model by integrating the previous studies to construct both the structural and the property model using commercial available software in the industry.
-
Phase-II Dynamic Model Construction:
EPTS team usually applies the conventional reservoir engineering concepts before start building the dynamic model. The objective of this study is to better understand the reservoir and to prepare the data for the simulation phase.
-
UP-SCALING:
EPTS team usually applies the conventional reservoir engineering concepts before start building the dynamic model. The objective of this study is to better understand the reservoir and to prepare the data for the simulation phase.
-
HISTORY MATCHING:
EPTS team will apply the most updated technology during the history match task of the study. All the team will work together trying to understand the reasons and the main parameters that affect the history match quality. If there will be a need to visit any of the previous tasks, the team will re-visit then apply this update and re-do all necessary work to update the dynamic model such as smooth and valid history match will be obtained at end of this task.
-
RESERVOIR PERFORMANCE PREDICTION:
Based on the objectives of the study EPTS team will perform all types of prediction scenarios for the field such as:
- Predict field performance with no actions taken.
- Predict field performance based on applying work-over campign.
- Predict field performance based on addition infill wells.
- Predict reservoir behavior with different drive mechanisms.
-
ECONOMIC STUDY:
Based on the prediction performance, the economic parameters and conditions that can be given to EPTS, Economic study will be performed so that the decision tree will be easy to be constructed.
PURPOSE OF THE STUDY:
Study development options such as natural depletion, water injection, and/or gas injection. Decide when to initiate a secondary recovery method to maximize oil recovery and select pattern type should be used. Select the appropriate type of EOR methods applied for an asset and what will be the EOR performance and its ultimate recovery? Investigate different well locations and spacing that will affect the ultimate recovery. Decide the critical data that have the most effect on recovery and, therefore, recommend proper actions.
SUMMARY
- Construct dynamic model based on the available static model and apply EPTS checklist process.
- Build simulation grid that are consistent with the structural geology and flow directions
- Incorporate reservoir complex features
- Verify grid geometry/properties using EPTS QAQC process
- Perform detailed conventional RE studies to fine tune both the static and dynamic models.
CONSTRUCT DYNAMIC MODEL AND PERFORM THE FOLLOWING SENSITIVITIES:
- Faults
- PVT
- SCAL
- Perform EPTS history match technique
- Predict reservoir performance with different production scenarios
- Select the appropriate development option to maximize the ultimate recovery of the reservoir
- Perform economical feasibility study
Calculate the original hydrocarbon in place using probabilistic approach. Define 1P, 2P and the 3P OIP cases. Estimate the ultimate reserves as 1P, 2P and 3P cases. The developed produced and non-produced reserves by applying material balance and advanced decline curve analysis. calculate the undeveloped reserves and propose developed plan to develop these reserves.
Client : Kuwait Energy Egypt “KEE”
Project: : East Ras Qatar, Burg El-Arab, Abu-Sennan, and Area-A Oil Fields Reserves Estimate Study
Value : By applying the top most technology in Oil & Gas industry in this project, KEE managed to achieve the following:
Created consistent methodology for calculating the reserves for their assets. Categorize the reserves as per the standard guide lines by the society of petroleum engineers Society of Petroleum Engineering – Petroleum Resource Management System (SPE PRMS) dated March 2007”. On job training for their engineers.
Client : Gemsa Oil Company “GEMPTCO”
Project: : Zaafarana Water Management Study
Value : By applying an integrated workflow between the subsurface team, the client managed to:
Determine which zones in the reservoir those have potential to be completed, Determine which areas in the reservoir that have bypassed oil, Determine best location for infill drilling.
Client : VE-GAS Company
Project: : Horus Engineering Study
Value : By applying an integrated workflow between the subsurface team, the client managed to:
Calculate the reserves for Horus oil field.
Categorize the reserves as per the standard guide lines by the society of petroleum engineers “Society of Petroleum Engineering – Petroleum
Resource Management System (SPE PRMS) dated March 2007”.
Determine which zones in the reservoir those have potential to be completed,
Determine which areas in the reservoir that have bypassed oil,
Determine best location for infill drilling.
On job training for their engineers.
The weakness or lack of Human Resources management is not too bizarre, in fact, it is a common problem facing most of the companies working in the MENA market, especially companies who are transiting from a small to a medium or large size business. It becomes more and more crucial as the company moves to more advanced and complex type of business. The only way to resolve such a problem is to develop a systematic way to institutionalize the Human Resources management, and ensure continuous development of adequate policies to attract and retain talented personnel, and to motivate them in their careers.
At IntelliGence, We provide end to end HR solutions. Our services start by mapping existing processes at the clients, followed by a complete gap analysis and assessment. We stand on the major gaps using world class benchmark tools and then customize a recommendation pack which we believe would boost the existing operation. Also, we get involved in the implementation, track development, and measure success criteria. We provide services to help your business embrace change and strengthen performance through proactive approaches to improving the organization and its most valuable assets, its people.
Exploiting the experience of Consultants whom have a long and successful career in Human Resources middle and high management positions, IntelliGence HR Consulting services include:
- Human Resources Policies and Procedures Manual
- Organization Restructuring and Job Profiling
- Establishment of HR Department
- Recruitment & Selection Process
- Training Needs Assessment and Training Plans
- Performance Appraisal and Improvement Plans
- Compensation and Benefits Programs
- Salary and Grading System
At IntelliGence, we help our clients recruit the best caliber available in the market. We predominantly focus on senior management since our strength lies in executive search & development. We have invested extensively in our people and robust processes to be recognized as one of the best recruitment firms in the region.
As far as technology is concerned, we use state of the art recruitment software. The database hosts tens of thousands of candidates' profiles in almost all sectors of industries and functions. Our team is fully trained to efficiently use the system in a way that fulfills our clients' needs at a timely manner and ensuring highest levels of customer service. We use various networking approaches to secure the most relevant candidates to fill our clients’ vacancies.
Additionally, we complement our recruitment business by selection & assessment consultancy services. This optional service includes competency based interviews, ability and psychometric tests, and case study tests for managers. This indeed helps leverage the process of recruitment and positions ahead of competitors.
We do work as below mentioned:
- Acquire Fresh Graduates and Experienced Candidates from all over the world.
- Assessment of their Skills, Education and experience according to job requirement.
- Our System start Fetching relevant companies for the candidate according their skills.
- Placement of interested candidates’ profiles to the MENA region based companies according the requirement.
- Follow-up of the Introduced profiles from the organizations.
- Conduct Online and Offline Interviews between Candidate and Firm.
Over the past 6 years GENCE has built a highly effective and successful Competency Assurance Management System (CAMS) that has been used to develop and train less competent employees for many industries including Oil and Gas.
Our partner’s main objective is the recruiting and development of local nationals to perform jobs to international competency standards. This results in permanently lowering operating costs and makes sustainable, and long-term contributions to the growth of the host country.
Through this process, GENCE has the ability and capability to assure our partners that each employee is trained to meet the competencies specified in the approved competency model for the job. The process can also be used to identify competency gaps of experienced employees and define custom training programs for each individual to eliminate any deficiencies. and define custom training programs for each individual to eliminate any deficiencies.
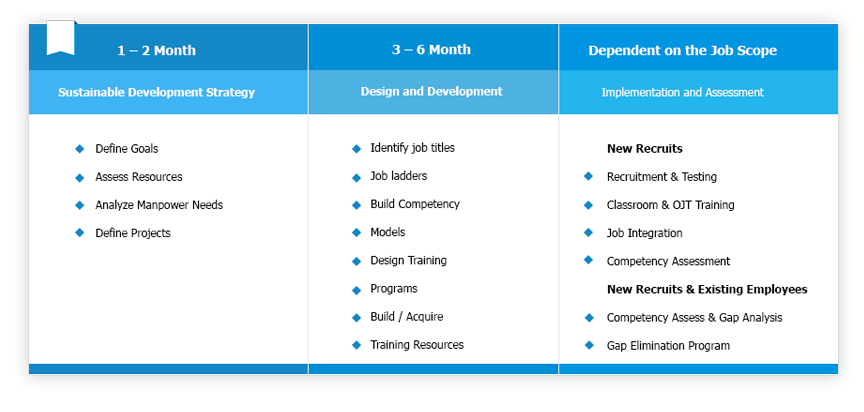
GENCE Consultancy and Training Services in strategic partnership with M&O group have developed a flexible and innovative process for design and implementation of Competency Assurance Management System (CAMS). The process is illustrated in the figure below:
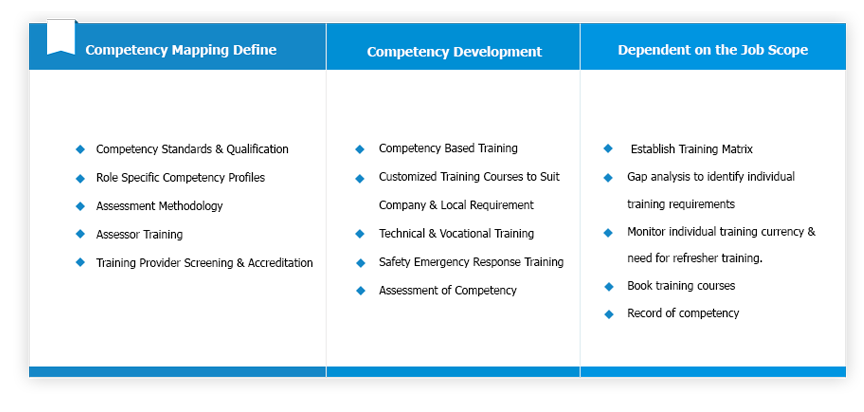
The result of effective competency mapping and management will enable our partners to develop and design internal control processes and ensure that employees have the required skills, knowledge and experience to perform their duties competently in their particular work environment.
- Competence Profiling
- Constructing Standards
- Assessment Services
- Human Resource Linkages
Competence profiling identifies the skills, knowledge & attributes that, when applied, lead to excellent performance on the job. Typically, these competencies can be grouped and integrated with each other into three key areas:

Competence Assurance Management System (CAMS) provides integrated solutions within an HR framework and responsibilities. It enables the HR personnel department to identify specific training needs and requirements in each discipline as shown in the diagram below: GENCE Competency Assurance Software.
GENCE qualified and experienced IT engineers together with competency assurance consultants have developed a customized (CAMS solution)® 5.0 software system which plans, organizes, and stores the information gathered, accelerates the information entry process and eliminate any paper work during the initial and final stages of implementation.
The software system enables the training coordinators, managers, training assessors and most importantly the staff themselves to create a specific profile for each of them with ability to monitor and track their training and development plan history and provide specific and targeted needs and requirements to fill their gap analysis.minate any deficiencies.
The model below represents GENCE approach to assessment of competency for the purposes of competency. Competency assessment may also be used as part of a wider learning and development, professional progression and career and succession planning framework. This being the case, simplified assessment models may be more appropriate. Examples of our assessment solutions capability include:
Customised development of an assessment process which delivers organisational needs and requirements (assurance versus development). Customised development of assessment resources, including Common Assessment Tasks, Assessment Guidelines, and resources for both those undergoing and undertaking assessment.
Training of workplace assessors and training providers in the provision of workplace assessment give organizations important resources to implement CAMS without external assistance or expertise. Provision of workplace assessment services using GENCE team of registered and accredited workplace assessors.
GENCE extensive experience and achievements in designing and developing prescriptive and comprehensive assessment resources solutions will enable your organization to strengthen and maximize the competency level, skills and experience of your staff.
GENCE assessment solutions reflect the technical specifications of the competency standards against which performance is to be measured. Our unique techniques and methods will ensure that workplace assessors and training providers apply a consistent approach to assessment and that consistent outcomes are produced.
The nature and process of competency assessment will vary depending on the purpose of the assessment. Technical and HSE-critical competency require a robust and transparent assessment process that provides organizations with specialized and specific requirements.
GENCE training philosophy and policy are based on strong emphasis and recognition that in today’s industry, training forms an integral part of the company’s operations. Therefore, the correct identification of training standards and training needs, plus the implementation of the appropriate competency training programs, form a significant contribution to improving overall efficiency and maintaining safety standards.
GENCE CAMS objectives are to ensure all our partners in business regardless of their levels and positions receive the necessary and specific competency programs in management, behavioural and technical disciplines in order to:
Obtain the relevant knowledge, motivation and skills required to manage safely;
Obtain the relevant knowledge and skills to perform their jobs to the required standards;
Update and maintain personnel needs with regard to statutory industry training requirements;
Implement appropriate staff training programs;
Maintain overall efficiency while achieving the required safety standards
GENCE is also committed to the setting and implementation of training standards through our membership and involvement with the following establishments:
Global Safety Standard (GSS) by Marine and Offshore Limited (M&O) Offshore Petroleum Industry Training Organisation (OPITO) National Vocation Qualification (NVQs) Scottish Vocational Qualification (SVQs) General Certificate of Education (GCSEs) General National Vocation Qualification (GNVQs)
DO YOU HAVE ANY INQUIRY?
LET US HELP YOU WITH YOUR REQUIREMENT.

